Are you looking to develop, launch, or promote a new product? Then you should definitely get acquainted with product marketing.
Read this guide to learn all the basics of marketing a product.
What is product marketing
Product marketing is the process of researching, positioning, and promoting a new product. Its aim is to drive a product’s demand and promote its usage.
The customer is at the center of all product marketing activities. To create a successful product marketing strategy, a product marketer needs to have a deep understanding of the target customer, their wants, needs, and pain points.
He or she needs to create buyer personas and marketing materials, conduct a market analysis, plan a go-to-market strategy, create a product launch plan, and develop product messaging and positioning.
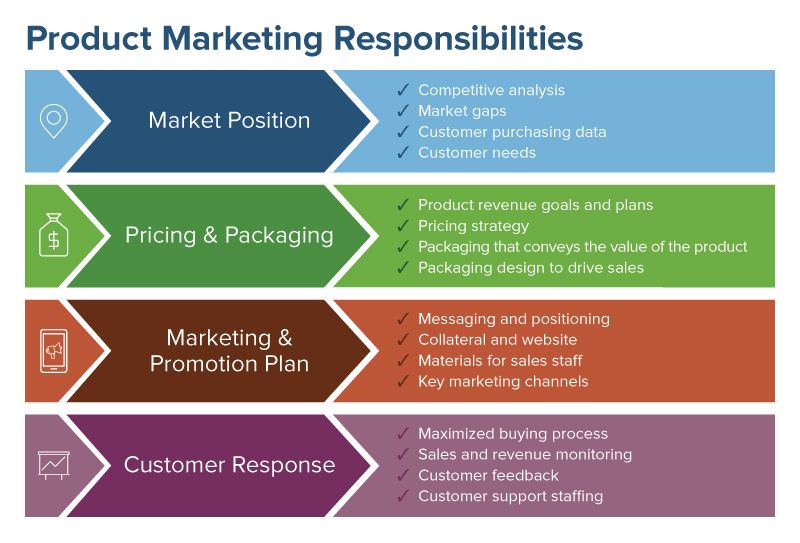
The importance of product marketing
Product marketing enables businesses to align their sales and marketing, gain a better understanding of their customers, target their buyer personas more effectively, and outperform their competition.
Product marketing vs. product management
While product marketing and product management are connected, they’re not the same.
Product management entails managing the product’s development and lifecycle.
It is responsible for gaining an understanding of market needs, leading product strategy and plans, as well as ensuring product alignment across different company departments.
Product marketing, on the other hand, is responsible for bringing a product to customers, which includes developing positioning and messaging, establishing competitive differentiation, and aligning sales and marketing teams.

Both of these processes start with the product vision, which is the essence and aim of a product. The product vision drives development, management, and marketing.
It’s most frequently described in a product vision statement, which answers questions such as:
- Is the product suitable for current market conditions?
- How does the product differ from similar competitors’ products?
- Who will use the product?
- What problems will the product solve?
- How will the product’s success be measured?
The four elements of product marketing
Product marketing consists of four distinct elements: brand strategy, product hierarchy, packaging, and positioning.
Brand strategy
Your brand strategy needs to outline how you can make your product offering clear and easy to understand, as well as describe a replicable structure for decision making that can be used as you scale your product line.
It determines how you’re going to apply your brand and its visual assets to your product. This includes your visual identity, voice, personality, and consistency.
Product hierarchy
Creating a product hierarchy involves:
- Organizing product modules and features into a meaningful framework, and
- Establishing a shared language.
This is to ease the sales process, guide product growth, and help to create a positive customer experience.
A product hierarchy provides options for explaining and selling a product at different stages of the buyer’s journey.
Packaging
Your product’s packaging helps buyers to quickly understand what they’re buying by grouping the product’s features in a way that will appeal to your target customers.
It should compel buyers to purchase the product.
Positioning
Product positioning aims to connect your product’s value with your target audience and serves as a supporting framework that enables consistent messaging across all your marketing channels.
It should address the way you solve your target audience’s pain points, and center on the benefits they stand to gain from using your product.
How to create a product marketing strategy
In this section, we’re going to talk about the entire process of creating a product marketing strategy, starting from performing market analysis to tracking and measuring results.
Perform market analysis
Performing market analysis is the first thing you need to do before creating a product marketing strategy.
The findings of your market research will influence both product development and positioning, as well as your overall marketing strategy.
The two main types of market analysis you’ll be employing in this stage include market research and competitive research.
A) Market research
Market research will show you if your product idea is viable in the current business environment while taking into account the buying habits in the industry and any existing competitors.

During this stage, you’ll want to gather data on your target audience with the help of interviews, focus groups, group surveys, as well as external sources of data such as journals, databases, and various online publications.
This will help you determine how many potential customers exist for your product and if they can afford it, which, in turn, will enable you to understand if your product idea is viable.
B) Competitive research
Competitive research revolves around analyzing products that are similar to yours, as well as their providers.
Its purpose is to identify your main competitors and reveal your product’s strengths, weaknesses, and differentiating factors.
In most cases, you’ll want to group your competitors into three categories:
- Primary competitors – Includes those that have the same product or audience as you (or both).
- Secondary competitors – Companies that sell a similar product to a different audience
- Tertiary competitors – Businesses that sell products that expand on your product.
You can collect data on your customers manually or use reports gathered by companies such as Nielsen, Wood MacKenzie, and NPD Group.
Define your target audience
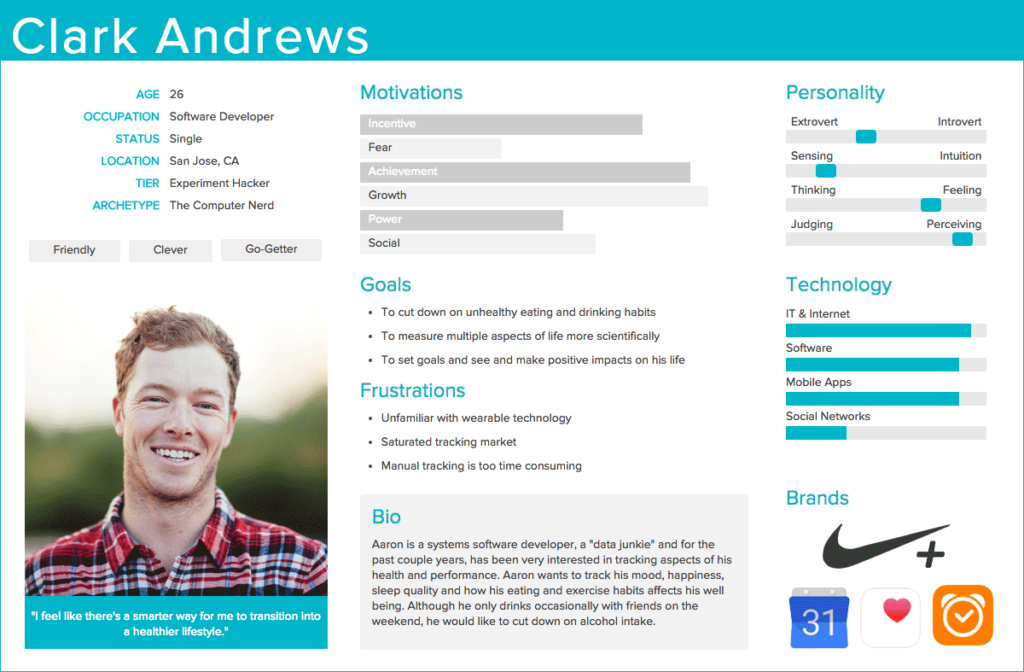
Armed with the data gathered from market research, you’ll now be able to define your target audience by creating detailed buyer personas.
Characteristics you’ll want to describe when defining buyer personas include age, gender, location, education, income level, goals, and pain points.
You should also include any other characteristics that might be relevant to your product.
Defining detailed buyer personas will allow you to create highly-targeted messaging that will give you the best chance of attracting and converting new customers.
Decide on your product’s positioning and messaging
The next step involves determining your product’s positioning and messaging. You’ll want to answer the following questions in this stage:
- Who is meant to use your product?
- What does your product do?
- In what way is your product different from competitors’ products?
This will help you to have an easier time describing your product and its benefits to your target audience as well as allow you to create a positioning statement that will help guide your marketing efforts.
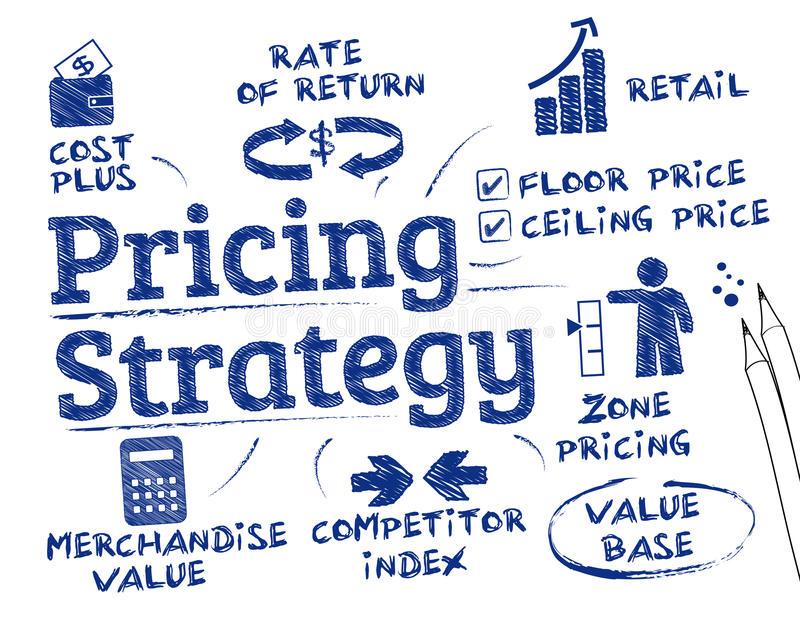
Choose a pricing strategy
After determining your product’s positioning and messaging, you’ll need to decide on a pricing strategy.
The two main strategies you’ll be looking to choose from include:
Competitive pricing – Involves looking at your competitors’ pricing and setting your prices to closely match theirs.
It’s mostly suitable for businesses that sell products that are almost identical to their competition’s offering.
Value-based pricing – This type of pricing strategy relies on setting your product’s price based on the value it provides to your target audience.
This is an especially profitable strategy for businesses that offer innovative or unique products.
Create a launch plan, a sales guide, and a promotion strategy
Before you can launch your product, you need to create a launch plan, a sales guide, and a promotion strategy.
Launch Plan
Your launch plan should include all the internal and external activities that need to take place during your product’s launch.
Its purpose is to give your sales team an insight into the product release timeline.
Sales Guide
The sales guide should serve to help the sales team sell your product by giving them an insight into the product and its features.
After studying the sales guide, your sales team should be able to answer any product-related questions a potential customer might ask.
Promotion Strategy
Creating a promotion strategy involves describing all the marketing channels that will be used to reach new customers, such as social media, email, and events.
You’ll also need to describe specific lead generation activities when creating your promotion strategy.
These will need to fit into your existing budget and resources.
Track, Measure, and Analyze Results
Once your product is launched, it’s crucial that you keep an eye on your results by tracking metrics such as
- Sales volume,
- Return on investment (ROI),
- Market penetration rate,
- Net Promoter Score (NPS), and
- Any other metrics that you deem relevant.
You should also gather and analyze feedback from your customers so that you can identify features you should add or eliminate from your product.
This will allow you to solve problems very early and improve customer retention.
Are you ready to get started with product marketing?
Product marketing involves researching, positioning, and promoting a product in order to drive demand and promote usage.
It helps businesses understand their customers better and have an easier time reaching their target audience.
The four main elements of product marketing include
- Brand strategy,
- Product hierarchy,
- Packaging, and
- Positioning.
When looking to create a product marketing strategy, the first thing you’ll need to do is perform market analysis.
This will allow you to gain a better understanding of your target audience, the current condition of the business environment, as well as your competition.
You’ll then need to define detailed buyer personas, decide on your product’s positioning and messaging, and choose a pricing strategy.
Before launching your product, you should also take the time to create a launch plan, a sales guide, and a promotion strategy.
This will help to increase your chances of success substantially.
After launching your product, it’s crucial that you track, measure, and analyze relevant metrics such as sales volume, ROI, market penetration rate, and Net Promoter Score.
This will enable you to improve your product and increase customer retention.