Figuring out how to monetize your startup is one of the most important aspects for all startup companies.
How are you planning to make a business of your idea? And how is it going to earn money?
25 Monetization Tactics
Without further ado, here are 25 monetization tactics that will help you better understand how to earn money from your online business/startup company:
I grouped the monetization tactics into five groups. Each group represents a more general business model, and the monetizations are the practical tactics that are used to generate revenue for each model.
When I came to define the business model for the purpose of this blog post, I asked the question:
What is the actual thing that is sold?
The answer to this question is the fundamental base of the product or service that is responsible for revenue generation.
The 5 groups, or fundamental revenue-generating bases:
- Advertising space base
- Agency base
- License/subscription base
- Lifestyle base
- Data base
Join my Facebook mastermind community
https://www.facebook.com/groups/StartupMarketingHeroes/

https://www.facebook.com/groups/StartupMarketingHeroes/
Advertising Space-Based Monetization Methods
Best fits content-heavy sites / apps, news magazines, mobile games, content based utility sites / apps.
-
Banner Ads:
This is the most basic model. A service provided for free to the user, how it’s exposed to advertisements while using the app/site. You pay for views or clicks on banners.
-
Affiliate Marketing:
Referring users to advertisers’ websites and driving them to complete a certain requirement (download app/software, fill a contact form, purchase something, etc). You are paid a fixed or commission-based payout for each successful completion of the requirement.
-
Offer Walls / Incentivized Traffic / Reward Ads:
This a sub-category of affiliate marketing that mostly fits mobile games developers. In this case, your users are incentivized to complete a certain action (download app/watch a video ad/etc) in exchange for a reward in game currency or other forms of virtual currency. You are paid a fixed price for each successful action.
-
Native Advertising:
AKA sponsored content, showing additional (“you may also be interested in”) content for your readers. The main advantage of native advertising upon banner ads advertising is that the native ads aren’t branded, and they keep a high level of credibility. This means that as a publisher who monetizes his content with native advertising, you may be more effective in generating revenues through referrals, and still be able to keep a high user experience of your site/app. Your are paid for each successful referral. The adverts are distributed by content distribution platforms such as Outbrain and Taboola.
-
Branded Content:
Basically, this means letting the advertiser create content on your site/app. For example, Coca Cola builds a whole level on a mobile app game.
-
Ad Free:
Allowing the user to pay a subscription fee in exchange for an ad-free experience. You are paid by your users for the advertisements you didn’t show them.
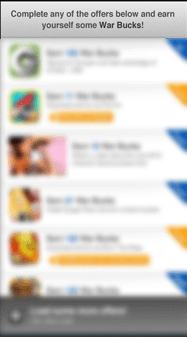
Offer Wall Example
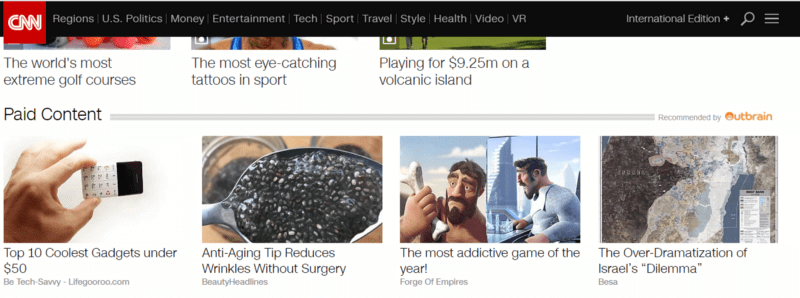
Native Advertising vie Outbrain Example
Agency-Based Monetization Methods
These models mostly fits marketplaces and platforms that get buyers and sellers together.
-
Commission:
Very common on marketplaces, such as Ebay, Roomer, Fiverr and others. You provide value to sellers and buyers by arranging an area where they can meet and conduct business. You are paid a commission on the transactions between the 2 sides.
-
Subscription Fee:
You give access to a database of sellers or buyers for a subscription fee. Mostly common on recruiting/HR platforms.
-
Pay to Offer:
You provide free access to a database of sellers and buyers but require a payment for the privilege of offering your service or posting a request for offers.
-
Pay to Get Noticed:
You provide free access to a database and to a communication platform. In order to gain more exposure for their offers, the sellers are allowed to bid for more exposure or a better placement.
-
Pay to List:
Common on merchandise marketplaces, such as Etsy. Free access for buyers; sellers are paying per each product they list.
-
Cashback:
Refer users to a third-party shopping website with a special coupon. The buyer receives a virtual currency refund for each purchase with the coupon, which they can use to generate more coupons.
This method is somewhere between the advertising-based and the agency-based models, and you can use this method on both.
License/Subscription-Based Monetization Methods
Usually fits to SaaS and B2B products or services, such as CRM, email marketing providers, data and analytics softwares.
-
Freemium:
An umbrella name for several pricing methods that are based on a basic usage level and product features that are free, when more advanced usability and features are paid.
-
Pay Per User:
For teamwork-oriented products. Each user costs an additional payment. Example: Slack.
-
Pay Per License:
Ideal for creative products or services, such as design and/or editing software. The method is based on international intellectual property laws and standards. You provide the product (video editing software for example) for free, but the user has to pay for usage license to be able to distribute its creation.
-
Pay Per Device:
Similar to the “per user” model. Each device (mobile, tablet or desktop) is given access for an additional fee. For instance, you can provide free access for the desktop app, but mobile is paid. Can be a good fit also for content-heavy products.
-
Pay What You Want (Tip Jar):
Get the whole service for any amount that you can afford starting at $0. Usually used by non-profit organization but not only. Example: Wikipedia.
-
Free DIY or Paid DFY:
You give a completely free access to the software and all the features, but offer an expert’s assistance for pay. Example: Unsplash.
-
Virtual Goods Merchandise:
It’s almost the opposite of the previous model. Here, you give a service or software access for free, but special or advanced features that are required for the work are paid. Example: Canva.
Lifestyle-Based Monetization Methods
Best methods for big brands or communities (sports club fans for instance). Also very popular among artists, publicists, politicians or other celebrities.
-
Branded Merchandise/Lifestyle Merchandise:
You provide free access to the content or products, or you charge separately for that, but while the user is engaging with the content, you market other product lines to them (can be white label merchandise). Example: Evernote’s market. Although it was terminated, it was responsible for 30% of Evernote’s revenue. The reason for the shutdown was to allow the team to focus on their core product.
You can find celebrities adopting this model, such as Gary Vaynerchuk, politicians such Alexey Navalny of Russia, and large web magazines such as The Next Web.
-
Direct to Consumer:
This is not only a monetization method but also one of the main consumer phenomena of the last decade. The oligopolic CPG industry didn’t catch up fast enough with some digital trends, while companies, such as Warby Parker, Harry’s, and Dollar Shave Club, took advantage on the opportunity to cut intermediary distribution costs and provide premium products at lower costs.
Using this model, you monetize on the distribution costs that you don’t pay while delivering your product (CPG) directly to your client.
Data-Based Monetization Methods
Here, I feel that there is more to tell.
This method fits products with a huge user base, such as popular apps, popular heavy-content sites, or large shopping websites. They also require a technological capability to collect and analyze large amounts of data.
There are 2 main groups of methods: Direct and Indirect.
Direct is basically when you give a third-party direct access to your database to collect and use your data. Indirect is when you allow your user (the third-party) to use different analysis of your data without having access to the raw data, or collect its own first-party data.
-
DaaS (data as a service) — Direct method:
Similar to the subscription based SaaS products. You can apply all the models described in the second methods group.
-
Packed Data — Direct method:
Sell specific data such as email lists, custom audiences for advertising, etc.
-
DIY DaaS — Indirect method:
Subscription-based access to a data management and analysis tool where the user is collecting its own first-party data.
-
Optimization — Indirect method:
Analyze your users first-party data using your third-party collected data analysis.
In this post, you read about 25 different monetization methods. To find a method for your startup:
- You have to have a market fit for your product
- Answer this question: What do you get paid for? In my post, there are 5 possible answers: advertising space, brokerage, license, lifestyle and data
- Select a method from the list
- Did you learn something new?
If you liked the article, please share it with your friends
See ya!